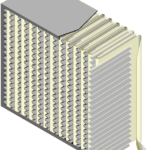
 HEPA filter stands for High Efficiency Particulate Air filter or High Efficiency Particulate Arrestance filter. HEPA filters are made of sheets with loosely and randomly interlaced fibers (diameter of fibres 0.65 – 6.5 micron, distance between them 10 – 40 microns). These sheets are collected into a “V” configuration and fixed into a rigid polyurethane frame. This design allows to increase specific surface area to capture maximum amount of extremely small dust particles sized 0.01 – 1 micron. Due to the highly absorbent pores of a HEPA air filter, particles cannot flow back into circulation. In some filters, area of filtration material can reach 40 square feet (3.7 m2).
HEPA filter stands for High Efficiency Particulate Air filter or High Efficiency Particulate Arrestance filter. HEPA filters are made of sheets with loosely and randomly interlaced fibers (diameter of fibres 0.65 – 6.5 micron, distance between them 10 – 40 microns). These sheets are collected into a “V” configuration and fixed into a rigid polyurethane frame. This design allows to increase specific surface area to capture maximum amount of extremely small dust particles sized 0.01 – 1 micron. Due to the highly absorbent pores of a HEPA air filter, particles cannot flow back into circulation. In some filters, area of filtration material can reach 40 square feet (3.7 m2).
Let’s learn more about the following topics:
How are HEPA filters classified?
HEPA filter must correspond the following conditions:
- The filtration material must be equally corrugated, which ensures efficient and even filtration on the whole surface. Otherwise, it would be difficult for airflow to pass through the filter with close-fitting folds.
- The filter frame must fit closely to the frame of vacuum cleaner, because airflow will follow the way with least resistance and filtration efficiency will be significantly reduced.
Types of HEPA filters
HEPA filters differ by material: washable (reusable) and non-washable (replaceable or disposable).
Washable HEPA filters are made of fiber fluoroplastic (expanded Poly Tetra Fluor Ethylene (ePTFE fibers)). It is a synthetic hydrophobic material. As a rule, manufacturers add porous activated carbon to the filtration material. It neutralizes odors, traps microscopic particles of dust and gasses from the air. Mainly, high class efficiency filters are made of this material.
Advantages of washable HEPA filters:
- Filtration material does not deform when wet (can be cleaned by water).
- Holding of dust particles sized 0.04-0.06 micron.
- Lasts longer than replaceable filter.
Disadvantages of washable HEPA filters:
- Expensive
- Residual moisture on the filter may cause mold, fungus and unpleasant odor, thus filter must be well dried after washing.
Replaceable (disposable) HEPA filters are made of layers of thin paper and fiberglass. Also some manufactures can use a lightweight cardboard as a filtration material. Therefore, it is prohibited to wash such filter, because it deforms immediately. It is also ineffective to clean it by blowing air because dust microparticles are retained in the filter fibers and cannot be cleaned. It is better to replace it with a new one.
Pros of non-washable HEPA filters:
- Do not obstruct airflow.
- Relatively cheap.
Cons of non-washable HEPA filters:
- Low wear resistance of filtration material. It is easy to damage the filter.
- Filtration material is deformed when wet.
- Skipping dust particles sized less than 0.3 micron.
To prevent reproduction of harmful microorganisms, some manufacturers can soak filtration material in special chemical composition. So, when buying a HEPA filter, we recommend asking about this.
How do HEPA filters work?
The main principles of HEPA filters are based on the following effects, which determine their effectiveness and performance:

Interception Effect Interception effect
This effect means an act or instance of intercepting something. According to this principle, it is sufficient for a particle to touch the filtration material to be caught by it. The main physics processes of this effect are adhesion and autohesion. Adhesion contributes to cling on clean fibers of filtration material, and autohesion helps to deposit already stuck particles. Thereby, particles make multilayered conglomerates. This principle is the most important for medium size particles (0.1-0.4 micron), since it is difficult for them to get out from airflow. This type of dust is named Most Penetrating Particle Size (MPPS).
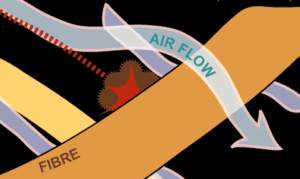
Diffusion Effect Diffusion effect
Such effect has the major influence on microparticles (less than 0.1 micron), because they have minor weight and hence always remain in the chaotic Brownian motion in the airflow. Their trajectory always changes relatively to the streamline. Consequently, the particle gets out from airflow, and touches the fibers, and settles.
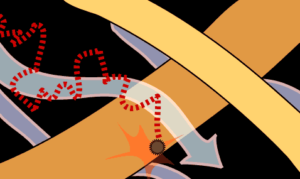
Effect of impaction (inertial effect)
Impaction Effect
It works on large, heavy particles (size more than 0.4 micron). Because of their weight, they are continuing to follow their trajectory, regardless of the change in air stream, until they touch the filtration material. This principle is reinforcing with space decrease between fibers and speed increase of airflow.
Sieving effect
This is the most popular mechanism of filtration. The effect is based on retention of particles (more than 1 micron) on the fibers, if they are larger than area between filaments. It has negative impact on HEPA filter, because large crumbs are blocking its pores, and the filter life time decreases. However, if you are using a pre-filter (for examples, vacuum bag, filter before the motor, canister of water, etc.), you can prolong the life of the HEPA filter.
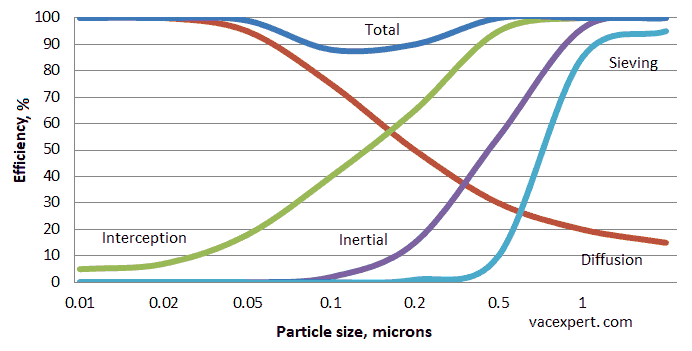
If we combine all these mechanisms in one graph, we can see that HEPA filter is more effective for capturing particles with size less than 0.1 micron and more than 0.4 micron, but the filter is less effective for mid-size particles (MPPS). This is the fundamental factor at classification of HEPA filters.
Classification of HEPA filters
HEPA filters are classified according to standards DIN EN 1822-1 and ISO 29463-1:
| Group | HEPA filter class | Collection efficiency by MPPS, % | |
| DIN EN 1822-1 | ISO 29463-1 | ||
| EPA * | E10 | – | ≥ 85 |
| E11 | ISO 15 E | ≥ 95 | |
| ISO 20 E | ≥ 99 | ||
| E12 | ISO 25 E | ≥ 99.5 | |
| ISO 30 E | ≥ 99.9 | ||
| HEPA | H13 | ISO 35 H | ≥ 99.95 |
| ISO 40 H | ≥ 99.99 | ||
| H14 | ISO 45 H | ≥ 99.995 | |
| ISO 50 H | ≥ 99.999 | ||
| ULPA ** | U15 | ISO 55 U | ≥ 99.9995 |
| ISO 60 U | ≥ 99.9999 | ||
| U16 | ISO 65 U | ≥ 99.99995 | |
| ISO 70 U | ≥ 99.99999 | ||
| U17 | ISO 75 U | ≥ 99.999995 | |
* EPA is an acronym which stands for Efficiency Particulate Air filters.
** ULPA is an acronym which stands for Ultra Low Penetration Air filters.
ULPA filters are more efficient than others, therefore they are being used in biochemical, electronic and space industries. However, due to complexity of production and higher quality control, they are much more expensive, hence are not being used for widespread products for common use, like vacuum cleaners. As a consequence, the most popular filters by ratio “price-quality” are filters of class E12, H13 and H14.
Some companies can classify filters as “HEPA-true” and “HEPA-type”.
“HEPA-true” (“True” or “Absolute” HEPA filter) means that a filter has a certificate from an independent laboratory and must capture more than 99.97% of MPPS. It may be important for Air Purification Systems in medical, space or other industries with high requirements of clean air. However, as a rule, it does not matter for home using. It is just a marketing term. “HEPA-type”, “HEPA-like”, “HEPA-style” or “99% HEPA” are being tested in manufacturers’ laboratories and can capture 85-99.9% of MPPS.
Cleaning a HEPA filter
Manufacturers recommend changing the dirty replaceable HEPA filter or washing the reusable HEPA filter. The service life of a filter depends on frequency of cleaning, area of a room, type of dust, pets, etc. Probably, if you use a vacuum cleaner every week for your whole house, the replaceable HEPA filter will last for about a year before it becomes too dirty. Nevertheless, in the similar conditions, the permanent HEPA filter could be used around 2 to 3 years before being replaced.
Indication of a dirty HEPA filter:
- Gray coating of dust on a filter.
- Suction power decreased and all pre-filters are clean.
- Vacuum cleaner motor is heating more than usual and all pre-filters are clean.
- Musty smell.
There are few cleaning methods depending on type of filtration material. As usual, type of HEPA filter is mentioned in the vacuum cleaner instruction or in the guide of the filter. Also washable HEPA filter can be indicated by the letter “W” in the model name. It is important to check material of HEPA filter before attempting to clean it.
How to clean washable HEPA filter?
In most cases, manufacturers recommend to rinse reusable HEPA filter with water at least monthly.
Steps of cleaning a washable HEPA filter:
- Remove a filter from a vacuum cleaner. If it is not clear how to do it, please refer the instruction of the vacuum cleaner.
- Use a vacuum cleaner hose with a brush to remove contaminants before washing. Or use a brush, but be gentle in order to not destroy the filter (it would be better doing it outside).
- Rinse your washable filter until water runs through it clearly. For more effective removing of grime, hold the filter under running cold water and along of pleats.
- Do not use detergents.
- Do not use machine wash.
- Let the filter dry at room temperature completely before reinstalling it (at least 48 hours). If the filter is wet, microparticles will be cemented in the filter fibers and thereby, filtration grade will be decreased. Also wetness could cause mold, fungus and disagreeable smell.
- Do not use dryer or heating equipment to accelerate dry.
If after the next washing of filter, the vacuum cleaner still overheats and its suction power still insufficient, then it is necessary to replace the HEPA filter.
How to clean paper HEPA filter?
Manufacturers recommend to change dirty filter and the following is usually written in a vacuum cleaner manual: “The filter CANNOT be washed as it will lose its dust trapping ability.” However, if you are still going to clean the replaceable HEPA filter, you can apply dry methods of cleaning (using air compressor or vacuum cleaner). It will prolong life of HEPA filter just a little bit.
Steps of dry cleaning of disposable HEPA filter:
- Remove a filter from a vacuum cleaner. If it is not clear how to do it, please refer the instruction of the vacuum cleaner.
- It is recommended to clean filter outside of a living area or in a garage, due to high amounts of dust.
- Gently tap it on a flat surface to remove some of a build-up of dust. Do not rub, because paper filter can probably tear or fall apart.
- Blow each pleat with air compressor from the back of a filter or use vacuum cleaner in front of a filter
The methods above can remove up to 80% of large dust particles (more than 1 micron). This dust is the main contaminant of a filter. Eventually, filter will be cleaned up to 80%. However, HEPA filters also capture external small particles (less than 1 micron), which could be removed for up to 30% and another 70% are still retained in the filter fibers. And after each next cleaning, the percentage of removed dust particles will be decreasing. Finally, it will result in a purchase of a new washable or non-washable HEPA filter.
Did you know?
HEPA filter was developed in the USA for the Manhattan Project in 1940s. It was used for capturing radioactive particles. However, today HEPA filters play one of the most important roles in keeping clean air in our homes, offices, stores and other locations. They are used in vacuum cleaners, air conditioners and ventilation systems to capture extremely small particles. These particles can be a cause of allergies and asthma, due to sedimentation in lungs. Therefore, HEPA filters are used in vacuum cleaners to capture dust particles and decrease influence of dust on the human health. It is important, because the device should not only collect dust, but also keep it inside.
In conclusion, HEPA filter is a necessary part of a vacuum cleaner, because it helps to save clean air at home and take care about the health of the family.
